What is Medicare?
Medicare is the federal health insurance program for people who are 65 or older, certain younger people with disabilities, and people with end-stage renal disease (permanent kidney failure requiring dialysis or a transplant, sometimes called ESRD). The different parts of Medicare help cover specific services:
Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance)
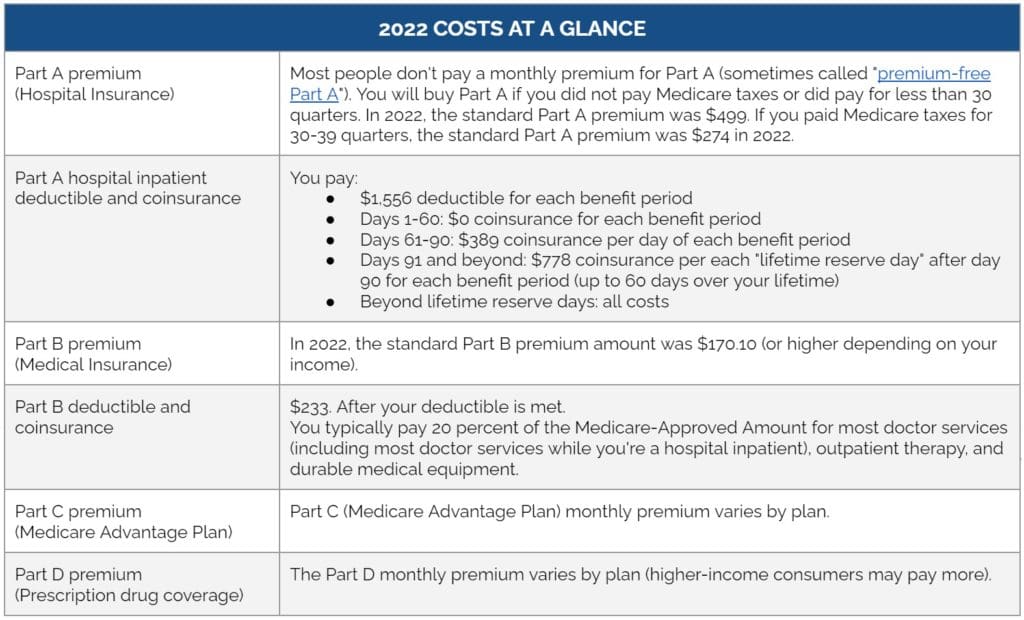
Part A covers inpatient hospital stays, care in a skilled nursing facility, hospice care, and some home health care. Most people do not pay a monthly premium for Part A.
You can get premium-free Part A at 65 if:
- You already get or are eligible to get retirement benefits from Social Security or the Railroad Retirement Board.
- You or your spouse has Medicare-covered government employment.
If you are under 65, you can get premium-free Part A if:
- You received Social Security or Railroad Retirement Board disability benefits for 24 months.
- You have end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and meet certain requirements.
 Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance)
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance)
Part B covers certain doctors’ services, outpatient care, medical supplies, and preventive services. Everyone pays a monthly premium for Part B. Most people will pay the standard Part B premium amount, which in 2022 was $170.10.
Medicare Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage)
Medicare drug coverage helps pay for prescription drugs you need. To get Medicare drug coverage, you must join a Medicare-approved plan (Part D) or a Medicare Advantage Plan with drug coverage.
Each plan varies in cost and the specific drugs covered, but plans must provide a standard level of coverage set by Medicare. Medicare drug coverage includes generic and brand-name drugs. What you will pay for each drug depends on which plan you choose.
How Does Medicare Work?
There are two main ways to get Medicare coverage.
1. Original Medicare
Original Medicare includes Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance) and Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance). You pay for services as you get them. When you get services, you’ll pay a deductible at the start of each year, and you usually pay 20 percent of the cost of the Medicare-approved service, called coinsurance. If you want drug coverage, you can add a separate drug plan (Part D).
2. Medicare Advantage (Often referred to as Medicare Part C)
Medicare Advantage is a Medicare-approved plan from a private company that offers an alternative to Original Medicare for your health and drug coverage. These “bundled” plans include Part A, Part B, and usually Part D. Plans may offer some extra benefits that Original Medicare doesn’t cover — like vision, hearing, and dental services. Medicare Advantage Plans have yearly contracts with Medicare and must follow Medicare’s coverage rules. The plan must notify you about any changes before the start of the next enrollment year.
 How Medicare Works with Other Insurance
How Medicare Works with Other Insurance
If you have Medicare and other health insurance (from a group health plan, retiree coverage, or Medicaid), each type of coverage is called a “payer.” When there’s more than one payer, the “coordination of benefits” rules decide who pays first. The “primary payer” pays what it owes on your bills first, and then sends the rest to the “secondary payer” (supplemental payer) to pay. In some rare cases, there may also be a third payer.
State Health Insurance Assistance Program (SHIP)
To get help understanding the different components of Medicare, find your local SHIP.
Continue to see your Indian health provider.
Your Indian health clinic will always be there for you. If you do have insurance, let your clinic know. They can bill Medicare, Medicaid, employer or marketplace plans for the services they provide. This provides more health care dollars to fund services for your entire community.